명품 C++ Programming 교재 5장 함수와 참조, 복사 생성자 실습문제 풀이입니다. 개인 풀이이므로 더 효율적인 풀이가 있을 수는 있으나 문제에서 요구하는 출력 조건은 모두 맞춘 해답 코드입니다.
1. 두 개의 Circle 객체를 교환하는 swap() 함수를 call-by-reference 로 작성하라
// 실습 1번
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Circle {
int radius;
public:
Circle() :Circle(1) {}
Circle(int r) { this->radius = r; }
void show() { cout << "반지름 : " << radius << endl; }
};
void swap(Circle& a, Circle& b) {
Circle tmp;
tmp = a;
a = b;
b = tmp;
}
int main() {
Circle a(1), b(2);
a.show();
b.show();
swap(a, b);
a.show();
b.show();
return 0;
}
2. half() 함수를 작성하라. (main() 와 실행 결과를 보고)
// 실습 2번
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void half(double& n) { n /= 2; }
int main() {
double n = 20;
half(n);
cout << n;
return 0;
}
3. combine() 함수를 작성하라. (main() 와 실행 결과를 보고)
// 실습 3번
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void combine(string s1, string s2, string& s3) { s3 = s1 + " " + s2; }
int main() {
string text1("I love you"), text2("very much");
string text3;
combine(text1, text2, text3);
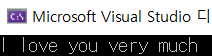
cout << text3;
return 0;
}
4. 원형이 주어진 bigger() 와 2개의 정수를 입력 받아 큰 값을 출력하는 main()을 작성하라. bigger()은 같으면 true, 다르면 false를 리턴하고 큰 수는 big에 전달한다.
// 실습 4번
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
bool bigger(int a, int b, int& big) {
big = (a >= b) ? a : b;
return (a == b) ? true : false;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
int big;
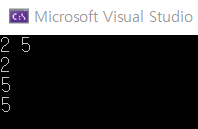
cin >> a >> b;
bigger(a, b, big);
cout << a << endl << b << endl << big << endl;
}
5. increaseBy() 함수를 수정하라.
// 실습 5번
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Circle {
int radius;
public:
Circle(int r) { radius = r; }
int getRadius() { return radius; }
void setRadius(int r) { radius = r; }
void show() { cout << "반지름이 " << radius << "인 원" << endl; }
};
void increaseBy(Circle& a, Circle& b) {
int temp = a.getRadius() + b.getRadius();
a.setRadius(temp);
}
int main() {
Circle x(10), y(5);
increaseBy(x, y);
x.show();
return 0;
}
6. find() 를 작성하라.
// 실습 6번
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
char& find(char a[], char c, bool& success) {
int i = 0;
while (a[i] != '\0') {
if (a[i] == c) {
success = true;
return a[i];
}
}
success = false;
}
int main() {
char s[] = "Mike";
bool b = false;
char& loc = find(s, 'M', b);
if (b == false) {
cout << "M을 발견할 수 없다" << endl;
return 0;
}
loc = 'm';
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
7. 스택 클래스 MyIntStack을 구현하라.
// 실습 7번
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyIntStack {
int p[10];
int tos;
public:
MyIntStack();
bool push(int n);
bool pop(int& n);
};
MyIntStack::MyIntStack() { tos = -1; }
bool MyIntStack::push(int n) {
if (tos < 9) {
p[++tos] = n;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyIntStack::pop(int& n) {
if (tos > -1) {
n = p[tos--];
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main() {
MyIntStack a;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
if (a.push(i)) cout << i << ' ';
else cout << endl << i + 1 << " 번째 stack full" << endl;
}
int n;
for (int i = 0; i < 11; i++) {
if (a.pop(n)) cout << n << ' ';
else cout << endl << i + 1 << " 번째 stack empty";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
8. MyIntStack을 수정하여 작성하라.
// 실습 8번
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class MyIntStack {
int* p;
int size;
int tos;
public:
MyIntStack();
MyIntStack(int size);
MyIntStack(MyIntStack& s);
~MyIntStack();
bool push(int n);
bool pop(int& n);
};
MyIntStack::MyIntStack() { tos = -1; }
MyIntStack::MyIntStack(int size) {
this->p = new int[size];
this->size = size;
this->tos = -1;
}
MyIntStack::MyIntStack(MyIntStack& s) {
this->size = s.size;
this->tos = s.tos;
this->p = new int[s.size];
for (int i = 0; i <= tos; i++) this->p[i] = s.p[i];
}
MyIntStack::~MyIntStack() { delete[] p; }
bool MyIntStack::push(int n) {
if (tos < 9) {
p[++tos] = n;
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool MyIntStack::pop(int& n) {
if (tos > -1) {
n = p[tos--];
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main() {
MyIntStack a(10);
a.push(10);
a.push(20);
MyIntStack b = a;
b.push(30);
int n;
a.pop(n);
cout << "스택 a에서 팝한 값 " << n << endl;
b.pop(n);
cout << "스택 b에서 팝한 값 " << n << endl;
return 0;
}
9. Accumulator 클래스를 구현하라.
// 실습 9번
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Accumulator {
int value;
public:
Accumulator(int value);
Accumulator& add(int n);
int get();
};
Accumulator::Accumulator(int value) {
this->value = value;
}
Accumulator& Accumulator::add(int n) {
value += n;
return *this;
}
int Accumulator::get() {
return value;
}
int main() {
Accumulator acc(10);
acc.add(5).add(6).add(7);
cout << acc.get();
return 0;
}
10. 참조를 리턴하는 코드로 append() 함수를 완성하여 프로그램을 작성하라.
// 실습 10번
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Buffer {
string text;
public:
Buffer(string text) { this->text = text; }
void add(string next) { text += next; }
void print() { cout << text << endl; }
};
Buffer& append(Buffer& buf, string text) {
buf.add(text);
return buf;
}
int main() {
Buffer buf("Hello");
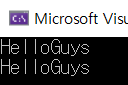
Buffer& temp = append(buf, "Guys");
temp.print();
buf.print();
return 0;
}
11. Book 클래스의 생성자, 소멸자, set() 함수를 작성하여 코드를 완성하라. (깊은 복사 생성자 추가하여), string 버전만 구현.
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Book {
string title;
int price;
public:
Book(string title, int price);
Book(Book& b);
~Book();
void set(string tile, int price);
void show() { cout << title << ' ' << price << "원" << endl; }
};
Book::Book(string title, int price) {
this->title = title;
this->price = price;
}
Book::~Book() { }
void Book::set(string title, int price) {
this->title = title;
this->price = price;
}
Book::Book(Book& b) {
this->title = title;
this->price = price;
}
int main() {
Book cpp("명품C++", 10000);
Book java = cpp;
java.set("명품자바", 12000);
cpp.show();
java.show();
return 0;
}
12. Dept 클래스를 완성하라
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Dept {
int size;
int* scores;
public:
Dept(int size) {
this->size = size;
scores = new int[size];
}
Dept(Dept& dept);
~Dept();
int getSize() { return size; }
void read();
bool isOver60(int index);
};
Dept::Dept(Dept& dept) {
this->size = dept.size;
this->scores = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < this->size; i++) {
this->scores[i] = dept.scores[i];
}
}
Dept::~Dept() {
delete[] scores;
}
void Dept::read() {
cout << "10개 점수 입력>>";
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
cin >> scores[i];
}
}
bool Dept::isOver60(int index) {
if (scores[index] >= 60) return true;
else return false;
}
int countPass(Dept dept) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dept.getSize(); i++) {
if (dept.isOver60(i))count++;
}
return count;
}
int main() {
Dept com(10);
com.read();
int n = countPass(com);
cout << "60점 이상은 " << n << "명";
return 0;
}
2번, 3번 주석 문제에 대해서 countPass 함수가 호출될 때 call-by-value 로 호출되기 때문에 복사 생성자가 호출되고, 복사 생성자가 없으면 오류가 발생합니다. 배열인 scores 가 얕은 복사로 이루어지기 때문이죠. 따라서 복사 생성자를 없애고 이 코드를 돌리려면 복사 생성자를 없애고, countPass 함수만 참조 매개 변수를 가지도록 하면 됩니다.
int countPass(Dept& dept) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < dept.getSize(); i++) {
if (dept.isOver60(i))count++;
}
return count;
}
'C++ > PS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [C++ PS] 명품 C++ Programming 실습 문제 4장 풀이 (0) | 2023.07.07 |
|---|---|
| [C++ PS] 명품 C++ Programming 실습 문제 3장 풀이 (0) | 2023.07.04 |
| [C++ PS] 명품 C++ Programming 실습 문제 2장 풀이 (0) | 2023.07.03 |